Kubernetes - Installing Cilium CNI
Table of Contents
This post is part of our ongoing series on Kubernetes. This post focuses on installing Cilium as the CNI in a K3s cluster. While K3s includes its own default networking stack, Cilium provides an alternative that leverages eBPF for networking, security, and observability. This setup can be useful for scenarios requiring more granular network policies, improved performance, or deeper insights into cluster traffic.
This guide specifically targets installing Cilium in kube-proxy replacement mode, which eliminates the need for the standard kube-proxy component and allows Cilium to handle all service routing more efficiently using eBPF.
1. Disable K3s Components
The first step is to configure /etc/rancher/k3s/config.yaml to disable the default networking components that would conflict with Cilium:
1write-kubeconfig-mode: "0644"
2disable-kube-proxy: true
3disable-network-policy: true
4flannel-backend: none
5disable:
6 - servicelb
7 - traefik
This configuration:
- Disables
kube-proxy, as Cilium will replace its functionality - Disables the default
network-policyimplementation = Setsflannel-backendtononeto prevent the default CNI from starting - Additionally disables
servicelb(the default load balancer) andtraefik(the default ingress controller)
Next step is to remove the traefik manifest from the auto-deploy directory:
1rm /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/manifests/traefik.yaml`
After applying these changes, restart the K3s service to apply the configuration:
1systemctl restart k3s
For a complete clean slate, it’s recommended to reboot all cluster nodes. This ensures any lingering network configurations are cleared.
2. Install Cilium
Now we’ll proceed with installing the core Cilium components using the cilium CLI. This approach provides a streamlined installation experience compared to manually applying manifests:
1cilium install \
2--version 1.17.1 \
3--set=ipam.operator.clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList="10.42.0.0/16" \ --set=kubeProxyReplacement=true \
4--set k8sServiceHost=192.168.1.19 \
5--set k8sServicePort=6443
This command configures Cilium with the following critical parameters:
- Retains the IPv4 CIDR range of K3s (10.42.0.0/16) for pod addressing
- Enables full kube-proxy replacement mode
- Specifies the Kubernetes API server endpoint (required for kube-proxy replacement mode since internal service discovery depends on it)
3. Configure Cilium with Flux
To ensure our Cilium deployment remains consistent and follows GitOps principles, we’ll configure it through Flux CD. This allows us to declaratively manage the Cilium configuration and leverage automated reconciliation.
Create cluster/default/cilium.yaml
1---
2apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
3kind: HelmRepository
4metadata:
5 name: cilium
6 namespace: kube-system
7spec:
8 interval: 10m
9 url: https://helm.cilium.io
10---
11apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2
12kind: HelmRelease
13metadata:
14 name: cilium
15 namespace: kube-system
16spec:
17 releaseName: cilium
18 interval: 10m
19 chart:
20 spec:
21 chart: cilium
22 version: "1.17.1"
23 interval: 10m
24 sourceRef:
25 kind: HelmRepository
26 name: cilium
27 namespace: kube-system
28 values:
29 operator:
30 rollOutPods: true
31 nodeIPAM:
32 enabled: true
33 kubeProxyReplacement: true
34 ipam:
35 operator:
36 clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList: ["10.42.0.0/16"]
37 defaultLBServiceIPAM: nodeipam
38 nodePort:
39 enabled: true
40 k8sServiceHost: "192.168.1.19"
41 k8sServicePort: "6443"
42 envoy:
43 enabled: false
44 hubble:
45 relay:
46 enabled: true
47 ui:
48 enabled: true
This configuration includes several important customizations:
- Implements
nodeIPAMmode to associate Node IPs withLoadBalancerservices, crucial for clusters without an external load balancer - Enables
nodePortsupport to expose services on node ports ( which to be consumed by Ingress controller for traffic routed via the cloud server setup done in Kubernetes - Routing external traffic to local Kubernetes cluster ) - Sets
defaultLBServiceIPAMtonodeipam - Disables Envoy in
DaemonSetmode since the embedded proxy mode is sufficient for smaller clusters, reducing resource consumption - Enables Hubble (with both relay and UI components) for enhanced observability and traffic visualization
Lets commit and push these change to Git repository, and Flux will automatically apply the configuration to the cluster.
4. Verify Setup
Once the deployment has been reconciled, validate the Cilium installation with the following command:
1cilium status
2
3 /¯¯\
4 /¯¯\__/¯¯\ Cilium: OK
5 \__/¯¯\__/ Operator: OK
6 /¯¯\__/¯¯\ Envoy DaemonSet: disabled (using embedded mode)
7 \__/¯¯\__/ Hubble Relay: OK
8 \__/ ClusterMesh: disabled
9
10DaemonSet cilium Desired: 2, Ready: 2/2, Available: 2/2
11Deployment cilium-operator Desired: 2, Ready: 2/2, Available: 2/2
12Deployment hubble-relay Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
13Deployment hubble-ui Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
14Containers: cilium Running: 2
15 cilium-operator Running: 2
16 clustermesh-apiserver
17 hubble-relay Running: 1
18 hubble-ui Running: 1
19Cluster Pods: 24/24 managed by Cilium
20Helm chart version: 1.17.1
21Image versions cilium quay.io/cilium/cilium:v1.17.1@sha256:8969bfd9c87cbea91e40665f8ebe327268c99d844ca26d7d12165de07f702866: 2
22 cilium-operator quay.io/cilium/operator-generic:v1.17.1@sha256:628becaeb3e4742a1c36c4897721092375891b58bae2bfcae48bbf4420aaee97: 2
23 hubble-relay quay.io/cilium/hubble-relay:v1.17.1@sha256:397e8fbb188157f744390a7b272a1dec31234e605bcbe22d8919a166d202a3dc: 1
24 hubble-ui quay.io/cilium/hubble-ui-backend:v0.13.1@sha256:0e0eed917653441fded4e7cdb096b7be6a3bddded5a2dd10812a27b1fc6ed95b: 1
25 hubble-ui quay.io/cilium/hubble-ui:v0.13.1@sha256:e2e9313eb7caf64b0061d9da0efbdad59c6c461f6ca1752768942bfeda0796c6: 1
To verify that kube-proxy replacement is functioning correctly, use the following command to inspect the detailed status:
1kubectl -n kube-system exec ds/cilium -- cilium-dbg status --verbose
2
3...
4KubeProxyReplacement Details:
5 Status: True
6 Socket LB: Enabled
7 Socket LB Tracing: Enabled
8 Socket LB Coverage: Full
9 Devices: enp1s0 192.168.1.19 2402:a00:402:60a4:cf53:64d7:94f3:90bd 2402:a00:402:60a4:5054:ff:fec2:f7c8 fe80::5054:ff:fec2:f7c8 (Direct Routing), wg0 10.0.0.2
10 Mode: SNAT
11 Backend Selection: Random
12 Session Affinity: Enabled
13 Graceful Termination: Enabled
14 NAT46/64 Support: Disabled
15 XDP Acceleration: Disabled
16 Services:
17 - ClusterIP: Enabled
18 - NodePort: Enabled (Range: 30000-32767)
19 - LoadBalancer: Enabled
20 - externalIPs: Enabled
21 - HostPort: Enabled
22 Annotations:
23 - service.cilium.io/node
24 - service.cilium.io/src-ranges-policy
25 - service.cilium.io/type
26BPF Maps: dynamic sizing: on (ratio: 0.002500)
27...
28Encryption: Disabled
29Cluster health: 2/2 reachable (2025-03-11T08:57:33Z)
30Name IP Node Endpoints
31 192.168.1.19 (localhost):
32 Host connectivity to 192.168.1.19:
33 ICMP to stack: OK, RTT=255.745µs
34 HTTP to agent: OK, RTT=268.478µs
35 Endpoint connectivity to 10.42.1.34:
36 ICMP to stack: OK, RTT=211.23µs
37 HTTP to agent: OK, RTT=432.791µs
38 192.168.1.24:
39 Host connectivity to 192.168.1.24:
40 ICMP to stack: OK, RTT=196.433µs
41 HTTP to agent: OK, RTT=574.349µs
42 Endpoint connectivity to 10.42.0.68:
43 ICMP to stack: OK, RTT=510.047µs
44 HTTP to agent: OK, RTT=1.232687ms
45Modules Health:
46...
This confirms that all necessary service types are correctly supported by Cilium’s kube-proxy replacement functionality.
5. Accessing Hubble UI
Now that Cilium is successfully installed with Hubble enabled, lets access the Hubble UI to visualize and analyze your cluster network traffic. By default, the Hubble UI is only accessible from within the cluster, but cilium cli supports shortcut to portforward and access it.
1cilium hubble ui
2 Opening "http://localhost:12000" in your browser...
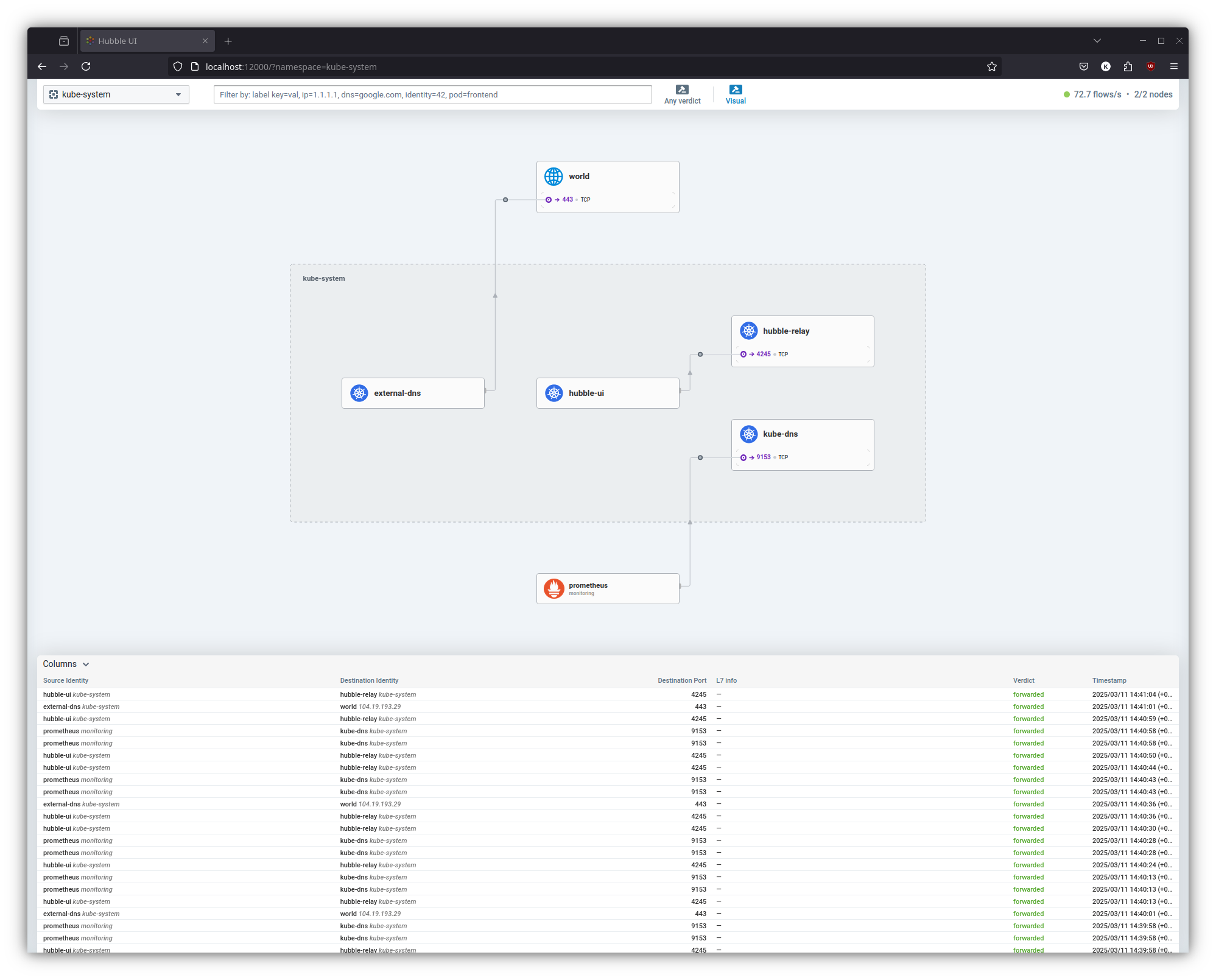
The interface provides detailed visualizations of pod-to-pod communication, service dependencies, and network policies enforcement.
References
- Cilium installation in K3s - https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/installation/k3s/
- Node IPAM LB - https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/node-ipam/