Kubernetes - Setup External DNS
Table of Contents
This post is part of our ongoing series of posts for Kubernetes. In this post we are focusing on setting up External DNS, a critical component for automating DNS record management. Although we are working on a local Kubernetes cluster, we have implemented prerequisites in Kubernetes - Routing external traffic to local Kubernetes cluster to enable access to our internal cluster via public ip.
We are using Cloudflare as our DNS Provider and implementing this solution using declarative GitOps principles with Flux.
1. Setup Cloudflare API Key
First, let’s generate an API key from Cloudflare by navigating to Manage Account > Account API Tokens in the Cloudflare dashboard.
We’ll choose Edit DNS template and generate token for a specific zone
2. Setup Kubernetes Secret
Now we’ll configure a Kubernetes secret by creating cluster/default/cloudflare-token.yaml
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Secret
3metadata:
4 name: cloudflare-token
5 namespace: kube-system
6type: Opaque
7stringData:
8 CF_API_TOKEN: ***
9 CF_API_EMAIL: ***
Let’s encrypt this sensitive data with SOPS and commit the changes to our Git repository.
4. Setup External DNS
Now we’ll configure the External DNS deployment by creating cluster/default/external-dns.yaml
1---
2apiVersion: v1
3kind: ServiceAccount
4metadata:
5 name: external-dns
6 namespace: kube-system
7---
8apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
9kind: ClusterRole
10metadata:
11 name: external-dns
12rules:
13- apiGroups: [""]
14 resources: ["services","endpoints","pods"]
15 verbs: ["get","watch","list"]
16- apiGroups: ["extensions","networking.k8s.io"]
17 resources: ["ingresses"]
18 verbs: ["get","watch","list"]
19- apiGroups: [""]
20 resources: ["nodes"]
21 verbs: ["list","watch"]
22---
23apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
24kind: ClusterRoleBinding
25metadata:
26 name: external-dns-viewer
27roleRef:
28 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
29 kind: ClusterRole
30 name: external-dns
31subjects:
32- kind: ServiceAccount
33 name: external-dns
34 namespace: kube-system
35---
36apiVersion: apps/v1
37kind: Deployment
38metadata:
39 name: external-dns
40 namespace: kube-system
41spec:
42 strategy:
43 type: Recreate
44 selector:
45 matchLabels:
46 app: external-dns
47 template:
48 metadata:
49 labels:
50 app: external-dns
51 spec:
52 serviceAccountName: external-dns
53 containers:
54 - name: external-dns
55 image: k8s.gcr.io/external-dns/external-dns:v0.14.2
56 args:
57 - --source=ingress
58 - --domain-filter=***
59 - --provider=cloudflare
60 resources:
61 requests:
62 memory: "64Mi"
63 cpu: "20m"
64 limits:
65 memory: "256Mi"
66 cpu: "200m"
67 env:
68 - name: CF_API_TOKEN
69 valueFrom:
70 secretKeyRef:
71 name: cloudflare-token
72 key: CF_API_TOKEN
73 - name: CF_API_EMAIL
74 valueFrom:
75 secretKeyRef:
76 name: cloudflare-token
77 key: CF_API_EMAIL
Explanation of External DNS Configuration
This YAML manifest consists of four Kubernetes resources that work together to enable automatic DNS record management:
-
ServiceAccount:
- Creates a dedicated service account named
external-dnsin thekube-systemnamespace - This provides an identity for the External DNS process to operate within the cluster
- Creates a dedicated service account named
-
ClusterRole:
- Defines the permissions required by External DNS to function properly
- Allows read-only access (
get,watch,list) to:- Services, endpoints, and pods: To monitor for changes to service endpoints
- Ingresses: To detect new or modified ingress resources
- Nodes: To gather information about the cluster nodes
-
ClusterRoleBinding:
- Associates the previously defined
external-dnsClusterRole with theexternal-dnsServiceAccount - This binding effectively grants the External DNS service the permissions it needs
- Associates the previously defined
-
Deployment:
- Creates the actual External DNS controller pod with specific configuration:
- Uses the
Recreatestrategy to ensure clean upgrades - Deploys the official
k8s.gcr.io/external-dns/external-dns:v0.14.2image - Configures important command-line arguments:
--source=ingress: Instructs External DNS to watch for Ingress resources--domain-filter=***: Limits DNS operations to a specific domain (redacted in the example)--provider=cloudflare: Specifies Cloudflare as the DNS provider
- Sets resource constraints to optimize performance:
- Requests modest resources (64Mi memory, 20m CPU)
- Sets reasonable limits (256Mi memory, 200m CPU)
- Injects Cloudflare credentials from the previously created secret:
CF_API_TOKEN: Authentication token for Cloudflare API accessCF_API_EMAIL: Associated email for the Cloudflare account
- Uses the
- Creates the actual External DNS controller pod with specific configuration:
With this configuration, External DNS will continuously monitor the Kubernetes cluster for new or modified Ingress resources. When it detects changes, it automatically creates, updates, or deletes the corresponding DNS records in Cloudflare according to the annotations and specifications in those resources. This eliminates the need for manual DNS management and ensures that your services are always accessible via their correct domain names.
Let’s commit these changes to our Git repository and verify that External DNS is deployed successfully.
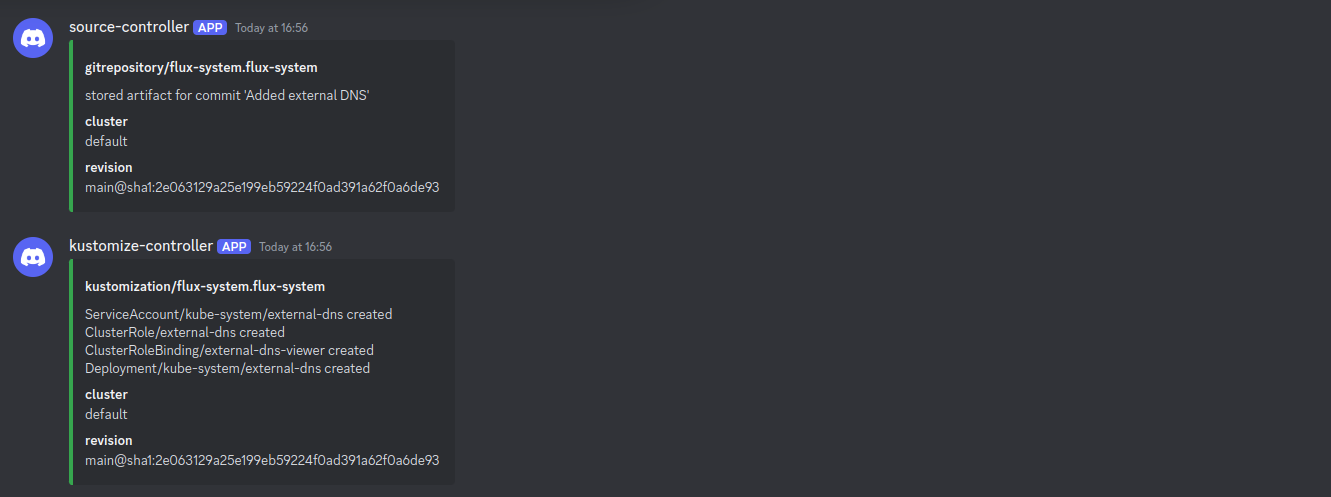
As we can see from the notifications in Discord, External DNS has been configured successfully.
Let’s examine the pod status as well:
1kubectl -n kube-system get pods
2
3NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
4coredns-ccb96694c-s67q5 1/1 Running 4 (60m ago) 4d2h
5external-dns-7cbfcc8d94-zwck7 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
6helm-install-traefik-8q42l 0/1 Completed 1 4d2h
7helm-install-traefik-crd-nq5tj 0/1 Completed 0 4d2h
8local-path-provisioner-5cf85fd84d-pxdcv 1/1 Running 4 (60m ago) 4d2h
9metrics-server-5985cbc9d7-qn4dr 1/1 Running 4 (60m ago) 4d2h
10svclb-traefik-aadbbe88-gjtbx 2/2 Running 8 (60m ago) 4d2h
11svclb-traefik-aadbbe88-vzd2t 2/2 Running 6 (60m ago) 4h10m
12traefik-5d45fc8cc9-g97pg 1/1 Running 4 (60m ago) 4d2h
As confirmed, External DNS is up and running. Let’s verify the logs to ensure proper functionality:
1kubectl -n kube-system logs pod/external-dns-7cbfcc8d94-zwck7
2
3time="2025-02-28T11:26:25Z" level=info msg="Instantiating new Kubernetes client"
4time="2025-02-28T11:26:25Z" level=info msg="Using inCluster-config based on serviceaccount-token"
5time="2025-02-28T11:26:25Z" level=info msg="Created Kubernetes client https://10.43.0.1:443"
6time="2025-02-28T11:26:27Z" level=info msg="All records are already up to date"
7time="2025-02-28T11:27:27Z" level=info msg="All records are already up to date"
8time="2025-02-28T11:28:28Z" level=info msg="All records are already up to date"
The logs indicate that External DNS is functioning properly.
5. Verify Setup
Now we’ll validate our setup by configuring an ingress for a sample application we created in Kubernetes GitOps with FluxCD - Part 3 - Automated Image Updates.
First, let’s configure a service by creating apps/sample-app/service.yaml
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: sample-app-service
5 namespace: default
6spec:
7 ports:
8 - name: http
9 protocol: TCP
10 port: 80
11 targetPort: 8080
12 selector:
13 app: sample-app
Next, let’s configure the ingress by creating apps/sample-app/ingress.yaml
1apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2kind: Ingress
3metadata:
4 name: sample-app-ingress
5 namespace: default
6 annotations:
7 external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/target: "******"
8spec:
9 rules:
10 - host: sample-app.***
11 http:
12 paths:
13 - pathType: Prefix
14 backend:
15 service:
16 name: sample-app-service
17 port:
18 number: 80
19 path: /
Since we’re working with a local cluster, we’ve implemented a solution to route external traffic to our cluster as detailed in Kubernetes - Routing external traffic to local Kubernetes cluster. The public IP of our external server is specified in the external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/target.
Now, let’s modify the kustomization file at apps/sample-app/kustomization.yaml
1apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
2kind: Kustomization
3resources:
4 - deployment.yaml
5+ - service.yaml
6+ - ingress.yaml
Let’s commit these changes and verify that External DNS has created the necessary DNS records:
1kubectl -n kube-system logs pod/external-dns-7cbfcc8d94-zwck7
2
3time="2025-02-28T11:42:34Z" level=info msg="Changing record." action=CREATE record=**** ttl=1 type=A zone=****
4time="2025-02-28T11:42:35Z" level=info msg="Changing record." action=CREATE record=**** ttl=1 type=TXT zone=****
5time="2025-02-28T11:42:35Z" level=info msg="Changing record." action=CREATE record=**** ttl=1 type=TXT zone=****
The logs confirm that the DNS records have been successfully created.
Finally, let’s verify access to our application using curl:
1curl http://sample-app.**
2
3Greetings From K8S App : Version 2
We have successfully configured External DNS, automating the creation and management of DNS records for our Kubernetes services.
What next ?
Future posts will explore advanced Kubernetes and GitOps patterns with FluxCD, including:
- Setting up Cert Manager
- Push based reconciliation triggers with Webhook receivers for FluxCD
Stay tuned for each of these topics.
References
- Kubernetes Documentation - https://kubernetes.io/docs/
- External DNS Documentation - https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/external-dns/latest/
- FluxCD Documentation - https://fluxcd.io/docs/